Rigid polyurethane insulating foam makes a major contribution to sustainability and eco-design by reducing the energy required to keep refrigerators and freezers cold.
Polyurethane rigid foam is the insulating material which is most widely used throughout the world for refrigerators and freezers. The insulation efficiency of polyurethane foams is a key property for the low temperature preservation of food during processing, storage and distribution to the consumer. Without polyurethane insulated refrigeration, approximately 50% percent of the world’s food would rot, heavily influencing our daily life and food related business.
Polyurethanes are ideal for the insulation of refrigerating appliances and have major advantages as they are:
- excellent insulators
- structurally strong thanks to the rigidity of the foam and adhesion of external skins (plastic and metal)
- the most cost-effective manufacturing solution, with multiple operations combined into one
- effective in confined spaces, allowing the maximum amount of food to be stored
- safe
- robust and strong
- very light, thus reducing transportation costs
- affordable, keeping the costs of refrigerators and freezers down
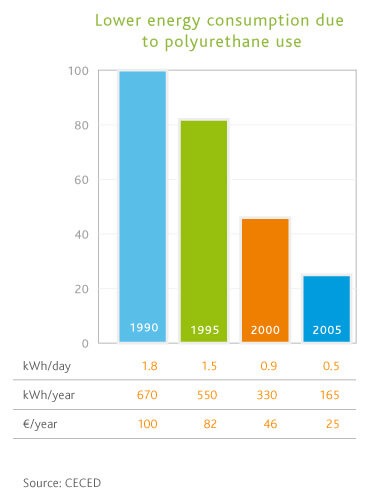
This means that ever more stringent energy standards can be met, with benefits to the consumer through lower energy bills and a reduction in energy used. As shown below, EU energy efficiency initiatives have resulted in considerable energy savings since 1990.